The Role of Hormones in Emotional Stability: How Your Chemistry Shapes Your Calm
Introduction
Emotions may feel mysterious, but they’re not random. Behind every mood swing, burst of joy, or wave of anxiety lies a symphony of hormones — the body’s chemical messengers that communicate between your brain and body.
When your hormones are balanced, you feel calm, resilient, and emotionally centered.
When they fall out of sync, life feels unpredictable — like your mind is fighting against your body.
From cortisol to estrogen, serotonin to oxytocin, hormones influence how you think, react, and recover from stress. The key to emotional stability isn’t just mental discipline — it’s hormonal harmony. 🌿
Let’s explore how your hormones affect emotions, what happens when they’re imbalanced, and how to restore equilibrium through lifestyle, nutrition, and self-awareness.
Looking for supplements for Emotional Stability? Click here.
🧬 What Are Hormones?

Hormones are chemical messengers secreted by glands in your endocrine system — including the hypothalamus, pituitary, adrenals, thyroid, and ovaries/testes.
They regulate everything from sleep and metabolism to energy, focus, and mood.
When released into the bloodstream, hormones deliver precise signals to cells, telling them how to behave. Think of them as text messages between your organs — quick, powerful, and constant.
🧠 In emotional health, the most important hormones include:
Cortisol – stress response
Serotonin – mood balance
Dopamine – motivation and reward
Estrogen and Progesterone – emotional regulation
Testosterone – drive and confidence
Oxytocin – connection and empathy
Thyroid hormones – energy and cognitive function
These chemicals don’t work in isolation — they form a dynamic network of balance that shapes your inner world.
🌊 The Endocrine–Brain Connection
The brain and hormones are in constant dialogue. The hypothalamus, located deep in your brain, acts as the conductor — monitoring stress, hunger, and emotional state, then directing hormone release through the pituitary gland.
This communication system is known as the HPA axis (Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal axis) when managing stress, or HPG axis (Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Gonadal axis) when controlling reproductive hormones.
When the brain detects imbalance — physical or emotional — it adjusts hormone output to bring things back to homeostasis.
The problem is, modern life constantly pulls that balance off center. Stress, poor diet, lack of sleep, and environmental toxins can disrupt your endocrine rhythm, making emotional calm harder to maintain.
🌿 Emotional balance begins where chemistry and consciousness meet.
⚡ The Hormones That Shape Your Emotional Landscape
Let’s explore how each key hormone contributes to emotional stability — and what happens when levels go off track.
🌤️ Cortisol: The Stress Regulator
Cortisol, produced by your adrenal glands, is often called the “stress hormone.”
In short bursts, it’s vital — helping you wake up, focus, and respond to challenges.
But when cortisol stays chronically high, it begins to damage emotional balance.
🧠 Effects of Balanced Cortisol
Steady energy throughout the day
Focus and motivation
Calm alertness under pressure
⚠️ Effects of Cortisol Imbalance
Anxiety, racing thoughts 😰
Fatigue or “wired but tired” feeling
Emotional irritability or burnout
Sleep disturbances
Chronic stress keeps the HPA axis in overdrive, flooding the brain with cortisol and desensitizing receptors. Over time, this leads to fatigue and mood instability.
🪷 How to Balance It:
Prioritize deep sleep
Practice breathwork and mindfulness
Limit caffeine and late-night screen use
Use adaptogens like ashwagandha or rhodiola for adrenal support
☀️ Serotonin: The Mood Stabilizer
Serotonin is the neurotransmitter most associated with happiness, contentment, and peace. It’s produced both in the brain and gut (about 90% in the gut).
Low serotonin is linked to depression, anxiety, and irritability, while balanced serotonin creates a sense of ease and self-confidence.
🧠 How Serotonin Affects Emotion
Regulates mood and anxiety
Promotes emotional flexibility
Supports sleep and digestion
⚠️ Signs of Low Serotonin
Sadness or hopelessness
Social withdrawal
Poor sleep
Sugar cravings
🧘 Ways to Support Serotonin:
Get morning sunlight (triggers serotonin production)
Exercise regularly
Eat tryptophan-rich foods (turkey, eggs, nuts, oats)
Take probiotics for gut health
Practice gratitude — it literally boosts serotonin levels 🌸
🔥 Dopamine: The Drive and Reward Hormone
Dopamine fuels motivation, pleasure, and curiosity. It gives you the “yes” feeling when you pursue goals or experience progress.
When dopamine is balanced, you feel focused and inspired.
When it’s low, life feels dull and aimless.
🧠 Healthy Dopamine Brings:
Motivation and focus 🎯
Joy and reward
Mental energy
⚠️ Low Dopamine Symptoms
Apathy or low drive
Procrastination
Addictive behaviors (scrolling, food, shopping)
Fatigue or brain fog
🧬 How to Balance Dopamine:
Break big goals into small wins to release dopamine naturally
Get 7–9 hours of sleep
Avoid overstimulation (limit constant social media dopamine hits)
Eat tyrosine-rich foods (avocado, eggs, fish)
Supplements: L-tyrosine, magnesium, CoQ10 for energy support
💡 Healthy dopamine flow = sustained motivation without burnout.
🌺 Estrogen: The Emotional Balancer (for Women)
Estrogen isn’t just about fertility — it profoundly affects mood, memory, and energy.
It helps regulate serotonin and dopamine, enhances blood flow to the brain, and supports emotional fluidity.
When estrogen levels fluctuate (as during PMS, postpartum, or menopause), emotional turbulence often follows.
🧠 Balanced Estrogen:
Emotional stability
Confidence and creativity
Cognitive sharpness
⚠️ Low Estrogen:
Low mood or apathy
Brain fog
Hot flashes and sleep disruption
Loss of motivation
⚠️ High Estrogen:
Irritability and anxiety
PMS mood swings
Fluid retention or bloating
🌸 Balance Estrogen Naturally:
Eat cruciferous vegetables (broccoli, kale, cauliflower)
Manage stress (high cortisol suppresses estrogen balance)
Avoid xenoestrogens (plastics, chemical fragrances)
Support liver detox with fiber and hydration
🩷 Estrogen is emotional intelligence embodied — powerful, intuitive, yet sensitive to balance.
🌙 Progesterone: The Calming Hormone
Progesterone works in harmony with estrogen to create emotional calm and deep sleep.
It’s known for its soothing effects — stimulating GABA, a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation.
When progesterone drops (often in the second half of the menstrual cycle or perimenopause), anxiety and insomnia often rise.
🧠 When Balanced:
Calm focus
Deep sleep
Emotional stability
⚠️ When Low:
Irritability or mood swings
Restless sleep or anxiety
PMS symptoms
🌿 Ways to Support Progesterone:
Reduce stress (cortisol competes for hormonal resources)
Maintain healthy body weight and cholesterol
Ensure zinc, magnesium, and vitamin B6 intake
Consider herbal support: chasteberry (vitex), ashwagandha
💪 Testosterone: The Confidence Hormone (for All Genders)
Though often associated with men, testosterone plays a vital role in both sexes.
It fuels motivation, assertiveness, and a sense of purpose — key ingredients in emotional strength.
🧠 When Testosterone Is Balanced:
Steady confidence
Strong focus
Positive outlook
⚠️ When Low:
Fatigue
Decreased motivation
Emotional flatness
Loss of resilience
🧬 How to Support It:
Strength training (naturally boosts testosterone)
Prioritize sleep and recovery
Eat healthy fats (olive oil, nuts, eggs)
Avoid excessive alcohol or sugar
Manage stress — cortisol suppresses testosterone
💥 Testosterone fuels the will to act; balance it, and life regains direction.
💞 Oxytocin: The Bonding Hormone
Oxytocin is the hormone of trust, connection, and empathy.
It’s released during physical touch, acts of kindness, and social bonding.
High oxytocin reduces stress, strengthens relationships, and promotes a sense of belonging — essential for emotional stability.
🧠 Benefits of Oxytocin:
Decreases anxiety
Improves communication
Boosts resilience to emotional pain
⚠️ Low Oxytocin:
Loneliness or detachment
Difficulty trusting others
Emotional numbness
💗 Ways to Boost It:
Hugs and physical affection 🤗
Acts of service or compassion
Time in nature or with pets
Deep, honest conversation
✨ Connection is chemistry — oxytocin turns empathy into peace.
🔆 Thyroid Hormones: The Mood–Metabolism Link
Thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) control metabolism and energy flow.
Low thyroid function slows brain activity, often mimicking depression or fatigue.
⚠️ Low Thyroid Symptoms:
Low energy
Depression-like mood
Weight gain
Brain fog
🧘 Support Thyroid Health:
Get enough selenium (Brazil nuts), iodine (seaweed), and zinc
Avoid chronic stress (cortisol suppresses thyroid hormone conversion)
Eat a balanced diet and rest adequately
🪷 Your thyroid sets the emotional tempo of your entire being.
🌿 Hormonal Imbalance and Emotional Disorders
Hormonal fluctuations are linked to many emotional challenges:
| Hormone | Emotional Effect When Imbalanced |
|---|---|
| Cortisol | Anxiety, burnout, emotional volatility |
| Estrogen | PMS, depression, irritability |
| Progesterone | Restlessness, insomnia, anxiety |
| Thyroid | Low mood, fatigue |
| Testosterone | Apathy, low confidence |
| Oxytocin | Loneliness, distrust |
| Serotonin/Dopamine | Depression, emotional flatness |
Balancing hormones is not just a physical task — it’s emotional self-care at the deepest level.
🧘 Lifestyle Habits for Hormonal and Emotional Balance
🌤️ Prioritize Sleep
Sleep is the master regulator of hormones.
During deep sleep, cortisol drops, growth hormone rises, and neurotransmitter balance is restored.
Tips:
Sleep 7–9 hours consistently
Keep your room dark and cool
Avoid screens an hour before bed
🍎 Eat for Hormonal Harmony
Food literally becomes hormones.
Focus on:
Protein (for neurotransmitter synthesis)
Healthy fats (for hormone production)
Colorful plants (for antioxidants)
Fiber (for estrogen detox)
Avoid:
Refined sugar
Trans fats
Processed foods
💬 Every bite tells your hormones how to feel.
🧘 Manage Stress
Chronic stress floods the system with cortisol, disrupting estrogen, progesterone, and thyroid function.
Try:
Breathwork 🌬️
Meditation or prayer
Nature walks 🌳
Journaling
Want to try Breathwork? Click Here.
🏋️ Move Intentionally
Exercise balances insulin, increases dopamine, and improves hormonal sensitivity.
Combine:
Resistance training 💪
Yoga or stretching 🧘
Walking or dancing for joy 💃
💞 Cultivate Connection
Relationships release oxytocin and lower cortisol.
Laugh, touch, and share — your hormones respond to love.
🌞 Honor Your Rhythms
Cortisol, melatonin, and sex hormones follow circadian rhythms.
Respect your body’s natural cycles: wake with sunlight, wind down at night, and sync with your menstrual or energy rhythms.
🕰️ Your hormones thrive on predictability and compassion.
🌸 Nutritional and Herbal Support for Hormonal Balance
| Nutrient/Herb | Benefit | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Magnesium | Calms cortisol, supports progesterone | Leafy greens, nuts, supplements |
| Zinc | Aids testosterone and progesterone | Pumpkin seeds, oysters |
| Vitamin B6 | Supports serotonin, dopamine | Bananas, chickpeas |
| Omega-3s | Reduce inflammation and balance hormones | Fish, flaxseed |
| Ashwagandha | Lowers cortisol, improves thyroid | Supplement |
| Maca Root | Balances estrogen and energy | Powder or capsules |
| Vitex (Chasteberry) | Regulates progesterone and PMS | Herbal supplement |
| Rhodiola Rosea | Boosts energy and mood | Capsule or tea |
🌿 Always consult a professional before adding supplements, especially if on medication or hormone therapy.
Looking for supplements for Emotional Stability? Click here.
💫 Hormones and Emotional Intelligence

Emotional intelligence (EQ) — your ability to manage and understand emotions — is deeply influenced by hormonal stability.
Balanced serotonin and dopamine = optimism and focus
Regulated cortisol = calm decision-making
Healthy oxytocin = empathy and trust
Stable estrogen and progesterone = emotional fluidity
🧠 Hormonal balance enhances not just how you feel, but how you relate, respond, and recover.
🌺 Healing Hormonal Imbalance Through Self-Compassion
Hormonal fluctuations often make people blame themselves — for mood swings, tears, or exhaustion.
But these aren’t character flaws; they’re biological signals asking for care.
Rest when tired 💤
Nourish when depleted 🥗
Connect when lonely 🤝
Breathe when anxious 🌬️
“You are not moody — you are cyclical, rhythmic, alive.” 🌿
🌞 The Hormone–Resilience Connection
Emotional resilience — your ability to adapt and recover — depends on how efficiently your hormones reset after stress.
Balanced cortisol and serotonin bring flexibility.
Balanced estrogen and progesterone bring calm.
Balanced thyroid and testosterone bring focus and confidence.
Together, they create the emotional rhythm of resilience — the inner music that keeps you steady through life’s storms.
🌿 Resilience isn’t forced positivity; it’s hormonal harmony in motion.
🌿 Final Thoughts: Chemistry Meets Consciousness
Hormones are the bridge between your body and emotions.
They respond not only to what you eat or how you sleep, but to how you think, love, and breathe.
Balancing them isn’t about perfection — it’s about alignment.
It’s about creating a lifestyle that supports your natural chemistry instead of fighting it.
When your hormones are in sync, your emotions flow naturally: calm without suppression, energy without chaos, confidence without ego.
“Emotional stability isn’t the absence of feeling — it’s the harmony of hormones and heart.” 🌸
Looking for online therapy ? Click Here.
📚 References
McEwen, B. S. (2007). Physiology and neurobiology of stress and adaptation. Physiological Reviews.
Rubinow, D. R., & Schmidt, P. J. (2019). Sex hormones and mood in men and women. New England Journal of Medicine.
Raison, C. L., & Miller, A. H. (2017). The biology of stress and depression: Implications for treatment. Nature Reviews Immunology.
Owens, M. J., & Nemeroff, C. B. (1994). Role of serotonin in mood disorders. Annual Review of Pharmacology.
Filippi, M., et al. (2014). Neurobiology of oxytocin and its role in emotional regulation. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience.
Hampson, E. (2018). Estrogen, cognition, and emotion. Trends in Cognitive Sciences.
Saper, C. B. (2012). Hypothalamic regulation of sleep and circadian rhythms. Nature Reviews Neuroscience.
Manji, H. K. (2012). Neuroplasticity and mood stabilization. Molecular Psychiatry.
Panossian, A. (2010). Adaptogens in stress and hormone regulation. Pharmaceuticals.
Walsh, R. (2011). Lifestyle and emotional well-being: The integrative science of health. American Psychologist.
Related Posts
-

Nootropics That Promote Calm and Rest
Explore the world of calming nootropics — natural brain enhancers that promote relaxation, better focus, and deeper rest. Learn how L-Theanine, magnesium, ashwagandha, and other adaptogens help balance your nervous system, reduce stress, and support restorative sleep.
-

Best Natural Supplement Stack for Sleep
Discover the best natural supplement stack for deep, restorative sleep. Learn how nutrients like magnesium, L-theanine, glycine, and calming herbs such as chamomile and ashwagandha work together to relax your body, calm your mind, and improve sleep quality—naturally and safely.
-

Combining L-Theanine and Magnesium for Sleep: A Calm Night, Naturally
Discover how combining L-Theanine and Magnesium can help you drift into deep, restorative sleep. Learn how this natural duo calms the mind, relaxes the body, and supports your nervous system—without grogginess the next morning.
-

How to Sleep Better After Intense Workouts
Struggling to fall asleep after a tough workout? Learn how to optimize your post-training recovery with nutrition, hydration, and science-backed sleep strategies. Discover how to calm your nervous system, balance hormones, and wake up fully recharged for your next session.
-

Ashwagandha and Valerian: A Bedtime Combo for Deep Rest and Emotional Reset
Discover the calming synergy of Ashwagandha and Valerian root, two natural sleep aids that help quiet the mind, ease anxiety, and promote deeper rest. Learn how this herbal duo supports the nervous system, balances stress hormones, and restores emotional peace — without next-day grogginess.
-

How to Create a Resilience-Boosting Diet
Discover how to build emotional and physical strength from the inside out with a resilience-boosting diet 🍎. Learn which foods stabilize your mood, how supplements like magnesium and omega-3s strengthen your stress response, and why pairing nutrition with breathwork and therapy creates lasting calm, focus, and vitality 🌿💪.
-

Best Teas and Herbal Blends for Calmness: Nature’s Way to Restore Inner Peace
Ashwagandha, the ancient adaptogenic herb, helps your body find balance during stress. Known as “Indian ginseng,” it supports cortisol regulation, boosts energy, and restores calm clarity. Discover how this powerful root promotes resilience, emotional balance, and steady vitality — one cup at a time. 🌸
-

Parenting and Emotional Strength: How to Raise Children Without Losing Yourself
Empathy is the bridge that connects hearts — the quiet power to understand, feel, and support another’s emotions without judgment. Learn how empathy strengthens relationships, enhances communication, and cultivates deeper compassion in everyday life. 🌿
-

How to Bounce Back from Public Failure: Reclaiming Confidence, Purpose, and Power
Visualization is more than imagination — it’s brain training for resilience. By picturing calm, success, or healing, you activate the same neural pathways as real experience. Learn how daily visualization rewires your brain for confidence, emotional balance, and recovery from stress. ✨
-

Coping with Financial Stress Through Resilience: How to Stay Grounded When Money Feels Tight
Body awareness is the foundation of emotional resilience. By tuning into your body’s signals — tension, fatigue, or calm — you learn to recognize stress before it overwhelms you. Discover how mindfulness, gentle movement, and breathwork can deepen your connection with your body and restore balance from the inside out. 🧘
-

How to Stay Positive During Chronic Illness: A Guide to Emotional Strength and Hope
Creativity is more than art — it’s a form of healing. Whether through painting, writing, music, or small acts of expression, creativity helps release emotion, calm the nervous system, and reconnect you to joy. Discover how to use creativity as a tool for emotional balance, resilience, and self-discovery. 🌿
-

Resilience Tips for Caregivers: How to Stay Strong While Caring for Others
Joy isn’t the absence of pain — it’s the quiet strength to find light even in challenging times. Cultivating joy through small daily moments restores balance, releases stress, and reminds you of life’s beauty. Learn how to reconnect with authentic happiness, rebuild emotional energy, and nurture your nervous system through gratitude, presence, and play. 🌿
-

Building Resilience After a Breakup: How to Heal, Rebuild, and Rise Stronger
Social connection is one of the strongest predictors of emotional resilience. During difficult times, genuine relationships act as anchors — calming the nervous system, reducing stress hormones, and helping you regain perspective. Learn how cultivating real human connection can strengthen your mind, heart, and overall well-being. 🌿
-

How to Stay Emotionally Strong During Job Loss
Your emotions are powered by brain chemistry — a delicate balance of neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and cortisol. When these chemicals work in harmony, you feel calm, focused, and resilient. Learn how daily habits, nutrition, and mindfulness can support your brain chemistry and boost emotional well-being naturally. 🌿
-

Mitochondria and Emotional Energy: The Cellular Power Behind Your Mood
Breathwork is one of the most powerful tools for emotional regulation and cellular balance. Through intentional breathing, you can calm your nervous system, increase oxygen flow to the brain, and even support mitochondrial energy. Learn how conscious breathing connects body and mind — transforming stress into presence and emotional strength. 🌿
-

Inflammation and Its Impact on Mood Resilience: The Silent Link Between Body and Mind
Inflammation doesn’t just affect the body — it impacts the mind. Chronic inflammation alters brain chemistry, depletes serotonin, and makes emotional recovery harder. Learn how calming inflammation through nutrition, mindfulness, and sleep can restore balance, resilience, and a renewed sense of emotional strength. 💫
-

How Antioxidants Protect Emotional Well-being: The Hidden Link Between Oxidative Stress and Mental Health
Antioxidants do more than protect your body — they defend your mind. By neutralizing oxidative stress, antioxidants support serotonin, dopamine, and brain energy pathways that keep you calm, focused, and emotionally balanced. Discover how foods like berries, green tea, and dark chocolate nourish your brain, boost mood, and strengthen resilience from the inside out. 🌿✨
-
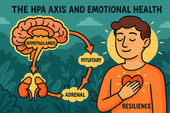
The HPA Axis and Emotional Health: The Hidden Bridge Between Stress and Mind
Neuroplasticity — the brain’s ability to rewire and adapt — is the foundation of emotional healing and resilience. When you face stress, trauma, or change, your neural pathways can reshape themselves to support new patterns of calm, focus, and self-awareness. Learn how daily practices like mindfulness, therapy, and breathwork strengthen neuroplasticity to transform emotional pain into personal growth. 🌸
-

Why Cortisol Control Is Key to Resilience: Mastering Stress to Build Emotional Strength
Controlling cortisol — the body’s main stress hormone — is the secret to lasting resilience. When cortisol levels stay balanced, your mind becomes clearer, emotions steadier, and energy more sustainable. Learn how breathwork, mindset shifts, adaptogens, and daily rhythms can help you calm your stress response and build true inner strength. 🌞💪
-

Dopamine’s Influence on Motivation and Recovery: Reigniting Drive and Balance
Healthy relationships are the foundation of emotional balance and resilience. Whether romantic, familial, or platonic, genuine connection releases dopamine, serotonin, and oxytocin — the brain’s “bonding trio” — helping us feel secure, motivated, and seen. Learn how trust, empathy, and communication not only strengthen your connections but also reshape your nervous system for deeper emotional well-being. 🌿🤝
-

The Role of Serotonin in Resilience: How This “Mood Molecule” Shapes Emotional Strength
Serotonin — often called the “resilience molecule” — plays a vital role in how we handle stress, regulate mood, and recover from emotional challenges. Beyond happiness, this powerful neurotransmitter helps balance the gut-brain axis, stabilize the nervous system, and support emotional flexibility. Learn how nutrition, sunlight, mindfulness, and adaptogens can naturally boost serotonin and strengthen your emotional resilience. 🌞🧠
-

How Neuroplasticity Supports Emotional Growth: Rewiring the Brain for Resilience
Neuroplasticity is the brain’s built-in power to grow, adapt, and heal — and it’s the foundation of emotional transformation. Every mindful breath, compassionate act, or reframed thought strengthens new neural pathways that support resilience and self-awareness. Learn how your brain rewires through daily habits, helping you turn emotional challenges into opportunities for growth and calm. 🌿
-

Tai Chi and Adaptogens for Mind-Body Balance: The Art of Harmonizing Energy and Resilience
Alchemy isn’t just an ancient science — it’s a timeless symbol of transformation and inner balance. By blending the physical and spiritual, alchemy teaches us that change begins from within. Just as metals are refined into gold, we too can transmute emotional pain, stress, and chaos into clarity and strength through mindful practice and self-awareness. 🌙✨
-

Cold Therapy and Emotional Control: Training the Mind Through the Body
Cold therapy isn’t just for athletes — it’s a tool for emotional mastery. By exposing your body to controlled cold, you train your nervous system to stay calm under stress, improving focus, mood, and resilience. This article explores the science of cold exposure, its impact on hormones and the vagus nerve, and how ice baths and cold showers can help you build emotional control, one breath at a time. 🧊🧘♂️
-

How Music Influences Emotional Recovery: The Healing Soundtrack of the Mind
Neuroplasticity — the brain’s ability to rewire and heal itself — is at the heart of emotional recovery. Through mindful habits, music, therapy, and consistent mental stimulation, your brain can form new connections that support resilience and well-being. Discover how neuroplasticity turns pain into growth, helping you rebuild balance, focus, and emotional strength. 🌿
-

Nature Therapy for Building Resilience: Reconnecting With the Healing Power of the Earth
Nature therapy helps rebuild emotional resilience by reconnecting you with the healing rhythms of the Earth. From forest walks to sunlight exposure, nature restores balance to your nervous system, lowers stress hormones, and teaches emotional adaptability. Learn how spending time outdoors can enhance mental clarity, calm anxiety, and awaken your natural capacity to heal. 🌞
-

Breathwork Techniques That Pair with Supplements: The Ultimate Synergy for Stress Relief and Mental Clarity
Breathwork and supplements create a powerful mind-body synergy for stress relief, focus, and energy. By combining intentional breathing with adaptogens, nootropics, and calming nutrients, you can naturally regulate cortisol, sharpen mental clarity, and boost emotional balance. This guide explores the best breathwork techniques and supplement pairings to help you feel centered, calm, and energized from the inside out. 🌿
-

Why Cortisol Balance Matters for Emotional Strength
Balancing cortisol — your body’s main stress hormone — is essential for emotional resilience. When cortisol is chronically high, your mind stays stuck in survival mode, leading to fatigue, anxiety, and emotional instability. This article explores how nutrition, supplements, breathwork, and therapy can help restore healthy cortisol rhythms, regulate the nervous system, and strengthen your ability to handle life’s challenges with calm focus and emotional strength. 🌿
-

Best Supplements for Students During Exam Season: Focus, Energy, and Memory Support
Studying late into the night? Learn which natural supplements can boost focus, memory, and mental stamina during exam season — without the crash. From omega-3s to Bacopa and Rhodiola, discover your brain’s ultimate exam support stack. 🎓🧠
-

Natural Memory Boosters for Seniors: How to Keep Your Mind Sharp and Focused
Stay mentally sharp and confident as you age. Discover science-backed natural supplements and lifestyle habits that boost memory, focus, and brain longevity for seniors. 🌿🧠
-

The Link Between Stress, Cortisol, and Memory Loss
Chronic stress can quietly erode your memory — and cortisol is the key culprit. Learn how stress hormones affect the brain, why the hippocampus shrinks under pressure, and how natural strategies can help you restore memory and mental clarity. 🧠✨
-

How to Build a Daily Supplement Routine for Memory Health
Want to sharpen your memory and stay mentally clear? Learn how to build a daily supplement routine for memory health — from morning focus to nighttime brain repair. Discover science-backed nutrients that boost recall, focus, and long-term cognitive resilience. 🧠🌿
-

Top 5 Natural Supplements for Memory Recall and Focus
Looking to boost memory and concentration naturally? Discover the top 5 supplements — Bacopa, Ginkgo Biloba, Lion’s Mane, Rhodiola, and Phosphatidylserine — that enhance focus, recall, and long-term brain health. 🧠✨
-

Top Supplements to Balance Mood Naturally
From omega-3s to adaptogens, discover the top natural supplements proven to support emotional balance, reduce stress, and promote inner calm — safely and effectively. 🌿✨
-

Can Omega-3 Fatty Acids Help with Mood Disorders?
Omega-3 fatty acids do more than support heart health — they can help balance mood, reduce depression, and calm anxiety. Discover how EPA and DHA nourish your brain, fight inflammation, and support emotional well-being from within. 🌊🧠
-

Vitamin D and Mood: The Sunshine Vitamin for Emotional Balance
Could the key to emotional balance be as simple as a little sunlight? Discover how vitamin D — the sunshine vitamin — influences serotonin, reduces inflammation, and helps you feel more positive and resilient year-round. ☀️💛
-

The Role of Magnesium in Reducing Irritability and Low Mood
Feeling on edge or emotionally drained? Magnesium could be the missing link between your body and your mood. Discover how this essential mineral reduces irritability, balances neurotransmitters, and helps your nervous system find calm again. 🌿✨
-
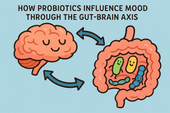
How Probiotics Influence Mood Through the Gut-Brain Axis
Discover how probiotics can do more than support your digestion—they can actually uplift your mood. This article explores the fascinating gut-brain axis and how balancing your gut bacteria through probiotics may help reduce anxiety, improve emotional stability, and support long-term mental well-being. 🌿🧠
-

Ashwagandha for Stress and Mood Regulation
Discover how Ashwagandha, the powerful adaptogenic herb 🌿, helps your body manage stress and regulate mood. Learn how it balances cortisol, boosts GABA and serotonin, and supports emotional stability — helping you feel calm, focused, and resilient every day.
-

St. John’s Wort: Natural Support for Mild to Moderate Depression
Discover how St. John’s Wort, the “sunshine herb” 🌼, naturally supports mild to moderate depression. Learn how it boosts serotonin, balances mood, and promotes emotional resilience — with research showing its effectiveness compares to antidepressants, but with fewer side effects.
-

Rhodiola Rosea and Mood Resilience Under Stress
Discover how Rhodiola rosea helps your body adapt to stress 🌿. Learn how this powerful adaptogen balances cortisol, supports serotonin and dopamine, and strengthens emotional resilience — helping you stay calm, focused, and energized under pressure.
-

Chamomile and Lavender: Herbal Calm for Emotional Fluctuations
Discover how chamomile and lavender bring calm to emotional ups and downs 🌿. Learn how these two soothing herbs balance your nervous system, ease anxiety, and support restful sleep — naturally helping you find peace and emotional stability.
-

Saffron Extract and Its Surprising Benefits for Mood Disorders
Discover how saffron extract — the golden spice of joy 🌸 — can naturally support mood balance, ease anxiety, and lift mild depression. Learn what science says about its serotonin-boosting power, the ideal dosage, and how this ancient remedy compares to modern antidepressants.
-

5-HTP and Serotonin: A Natural Path to Lifting Mood
Discover how 5-HTP naturally boosts serotonin 🌞 — the neurotransmitter behind mood, sleep, and emotional balance. Learn how this plant-derived compound supports happiness, reduces anxiety, and improves rest by helping your brain create more serotonin the gentle, natural way.
-
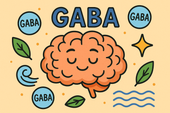
GABA Supplements for Reducing Anxiety and Mood Swings
Discover how GABA supplements can help reduce anxiety and balance mood naturally 🌿. Learn how this calming neurotransmitter works to quiet the mind, ease stress, and improve sleep — plus which nutrients and habits can boost your body’s own GABA production for long-term emotional stability.
-

L-Theanine for Calm Focus and Mood Stability
Discover how L-theanine, the calming compound found in green tea 🍵, promotes focus, relaxation, and mood stability. Learn the science behind how it balances neurotransmitters, reduces stress hormones, and enhances clarity — helping you stay centered, calm, and productive without sedation.
-

B Vitamins and Brain Chemistry: Supporting Energy and Emotional Balance
Discover how B vitamins power your brain chemistry ⚡. Learn how B6, B9, and B12 support serotonin, dopamine, and energy production — helping boost focus, mood, and emotional balance. From diet to supplements, explore how this vital nutrient group keeps your mind resilient and your energy steady.
-

N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC) and Mood Disorders: What the Research Says
Learn how N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC) supports brain health and mood balance 🧠. Discover how this antioxidant helps reduce oxidative stress, regulate glutamate, and improve emotional stability in depression, bipolar disorder, and anxiety — backed by cutting-edge psychiatric research.
-

Supplements for Bipolar Disorder: What May Support Stability
Discover the best supplements for bipolar disorder 🌿 that may support emotional stability and brain health. Learn how nutrients like omega-3s, magnesium, vitamin D, and NAC can help reduce inflammation, balance neurotransmitters, and complement traditional treatment safely.

















































